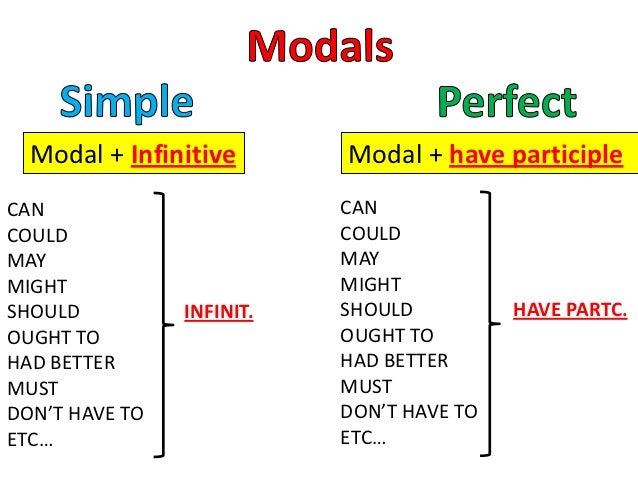
MODAL PERFECTS
Modal verbs, as we saw in the previous lesson, express possibility or probability. When used with the infinitive form of the perfect ("have" + past participle), modal verbs indicate speculation about things in the past.
Uses
Must have
Examples:
- The lights are off. They must have gone out.
- I never see John and Claire together anymore. They must have separated
- I know you love chocolate. It must have been difficult to say "no" to that piece of cake.
- John never called you last night? I must have been working late.
- Frank failed the exam. I have not been paying attention in class.
May have / Might have
"May have" and "might
have" are used to express possibility in the past. The use of these two
manners also expresses uncertainty.
Examples:
- I think it may have worked, but we gave up too soon
- They could have won if their star player had not been injured.
- I do not know, it might have been different if you were there.
Can’t have
"Can not have" is used in a
similar way to "must have", but in the negative way. We can use
"can not have" when we are fairly certain that something did not
happen or that it was not true in the past.
Examples:
- I know you love chocolate. It can not have been easy to say "no" to that piece of cake.
- Frank failed the exam. I can not have paid attention in class
- They had a lot of work to do and little time. They can not have finished everything.
Could have
"Could not have" can be used
instead of "can not have".
Examples:
- I know you love chocolate. It could not have been easy to say "no" to that piece of cake.
- Frank failed the exam. I could not have paid attention in class.
- They had a lot of work to do and little time. They could not have finished everything.
"Could have" is also used to
express that something was possible in the past but it did not really happen.
Examples:
- If it had not stopped raining, the party could have been a disaster.
- She could have run faster, but she wanted to save her energy.
"Could have", in the
affirmative, is similar to "might have" or "may have",
expresses possibility in the past.
Examples:
- I think it could have worked, but we gave up too soon.
- They could have won if their star player had not been injured.
- I do not know, it could have been different if you were there.
Should have / Ought to have
"Should have" and "ought
to have" is used when something did not happen, but it would have been
better if it had happened. In the negative, these referents indicate that
something happened, but it would have been better if it had not been like that.
Examples:
- I told you, you should have studied more!
- Ben ought to have gone to the doctor sooner. Now they say it will be a month before he's fully recovered
- We should have left earlier. Now we are going to be late.
- I should not have eaten that last cookie.
- She should not have been angry, it was not your fault.
Would have
"Would have" is used to form
conditional sentences in English.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Mhx23AV_Zc
modal perfects exercises
modal perfects exercises
Today's lesson is by Stephanie.

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario