FUTURE PERFECT
There are two main ways to express the future. Unlike the simple future, in the perfect time, the use of them is generally interchangeable.
Grammatical Rules
Structure
1. Affirmative Sentences
Sujeto + “will have” + participio pasado.
Sujeto + verbos auxiliar (to be) + “going to have” + participio pasado.
Example:
| The party will [is going to] have ended by the time you finish work. |
| I’ll [I’m going to] have eaten before we meet. |
2. Negative Sentences
Sujeto + “will” + “not” + “have” + participio pasado.
Sujeto + verbo auxiliar (to be) + “not” + “going to have” + participio pasado.
Example:
| The party won’t [isn’t going to] have ended by the time you finish work. |
| I won’t [I’m not going to] have eaten before we meet. |
3. Interrogative Sentences
“Will” + sujeto + “have” + participio pasado?
Verbo auxiliar (to be) + sujeto + “going to have” + participio pasado?
Example:
| Will [Is] the party [going to] have ended before you finish work? |
| Will [Are] you [going to] have eaten before we meet?
Uses
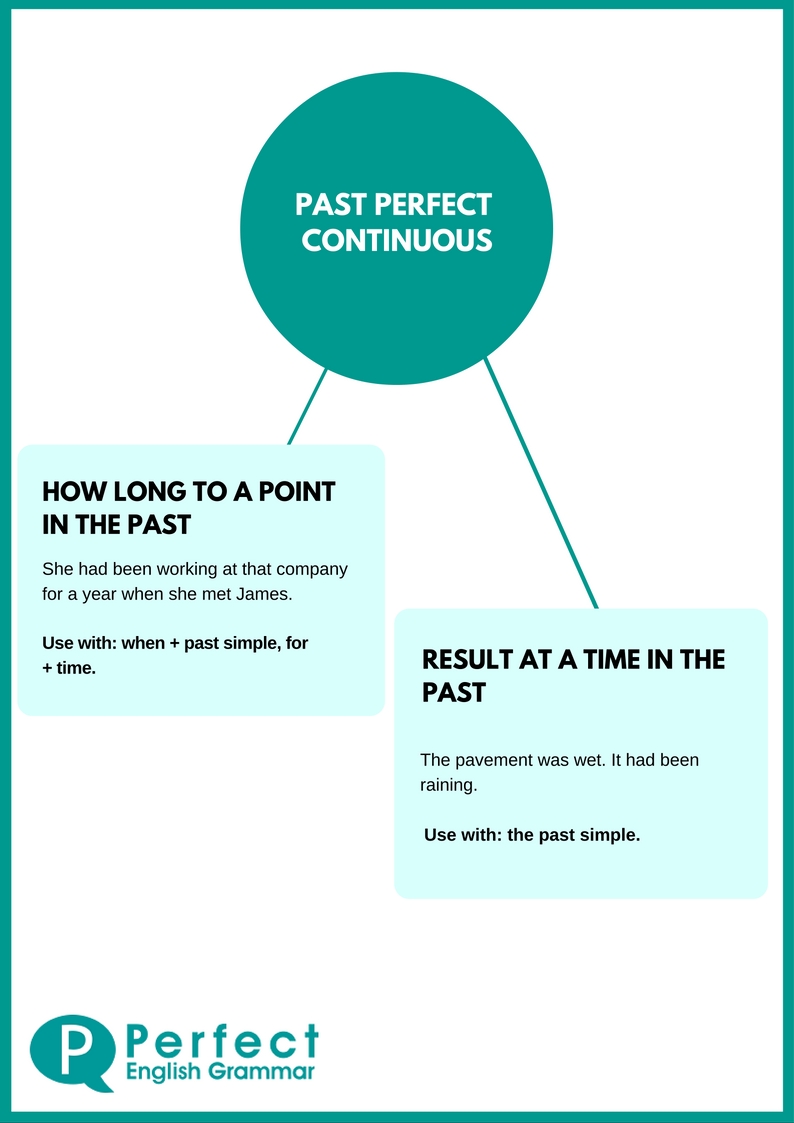
1. The perfect future is used for actions that will be finished before another action in the future. Also, it can be used to express that something will happen before a specific time in the future.
Example:
| I’ll have finished my studies before I start my new job. |
| Is Mike going to have trained enough before his first game? |
| We won’t have become fluent in Spanish by the time we leave for Mexico next month. |
2. We use the perfect future to show that something will continue until another action in the future.
Example:
| Karen is going to have worked for 50 years by the time she retires. |
| Next week, I’ll have lived in Germany for 1 year.
VIDEO STEPHANIE GÓMEZ
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8vf9XI89JZ0
Future Perfect – Exercise 01
Change the verb into the correct form, then press "Check" to check your answers. Use the "Hint" button to get a free letter if you don't know. Note that you will lose points if you ask for hints!
|
|